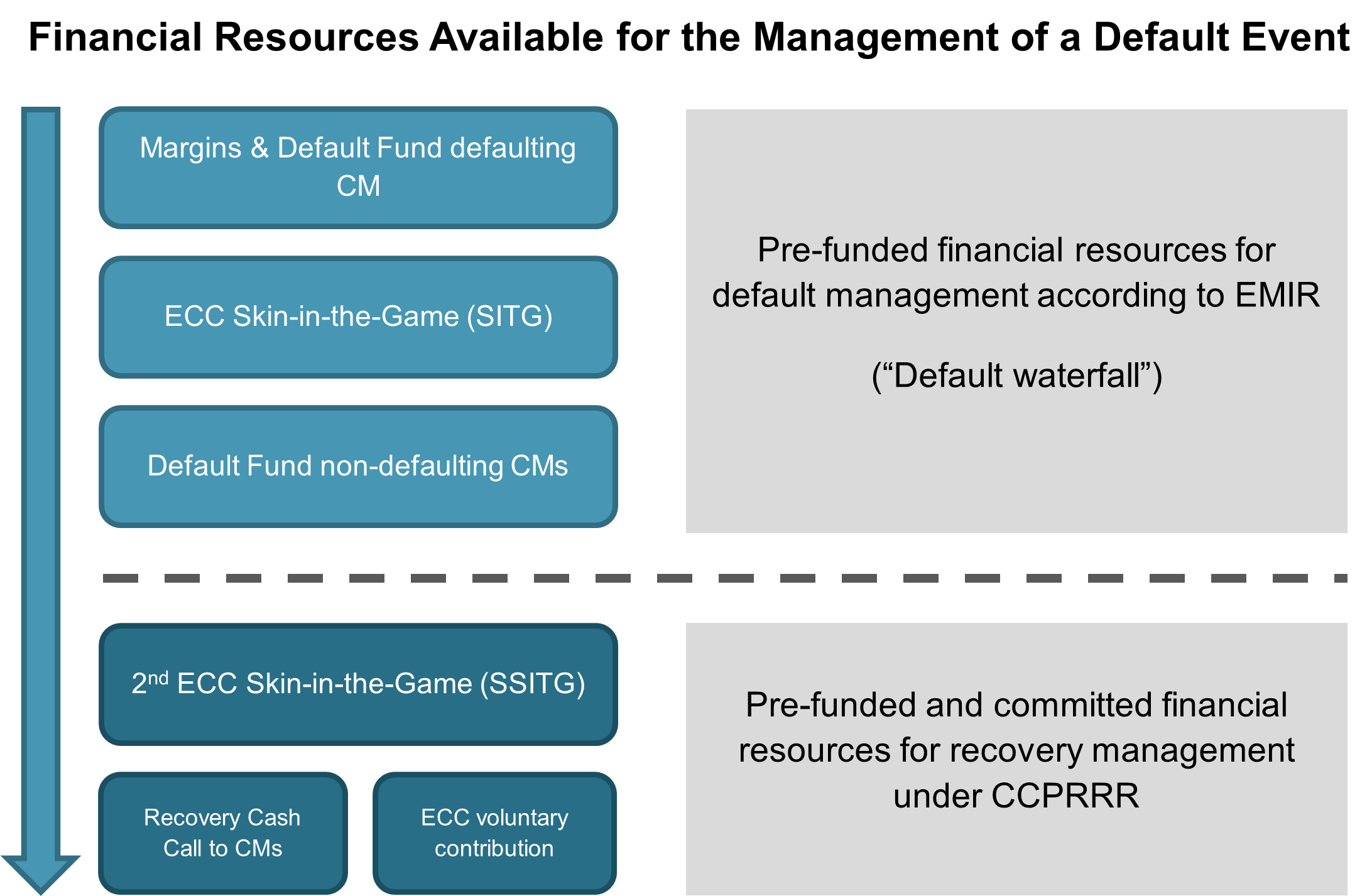
Lines of Defence
ECC’s capability to effectively manage risks is based on the various lines of defence:
1st Line of Defence: Clearing Member Admission Criteria
ECC operates under a principal-to-principal system, which means that participants trade through a Clearing Member. The Clearing Member guarantees the fulfilment of all requirements that result from its clients’ trades.
ECC has strict admission criteria to ensure that Clearing Members are financially sound and have robust operational processes and procedures in place to ensure adequate risk management of their clients. ECC monitors compliance with these requirements on a regular basis.
The first line of defence aims to minimize the risk of a potential Clearing Member default event.
2nd Line of Defence: Counterparty Risk Management Processes
ECC settles changes in profit and loss on a daily basis by paying out or collecting Variation Margin, thereby preventing risk from building up over time. In the case of large Variation Margins building up during the day (e.g., because of large positions being created or due to high volatility), ECC has the right to issue an Intraday Margin call. ECC uses limits to manage Clearing Members' derivatives exposure. For all its risk models, ECC calculates and updates relevant risk parameters on a daily basis.
3rd Line of Defence: Margin Collateral
Margin requirements are calculated according to ECC's margin methodology. Margin requirements are used to cover the risk from open positions on the derivatives markets and pending payments resulting from spot market deliveries with a confidence of 99% in the case of a default of the Clearing Member.
ECC uses additional margins to cover special risks from positions concentrations, delivery or intra-month stress test results. This line of defence aims at realizing the “defaulter pays principle” by using collateral posted by the defaulter to cover potential losses to ECC.
Information on ECC's margin collateral can be found in the current CPMI-IOSCO quantitative disclosure reports. Information on ECCs margin models is available at: Margining (ecc.de).
4th Line of Defence: ECC's Dedicated Own Resource
Also know as “Skin in the Game” (SITG). ECC holds dedicated, freely available and liquid equity to be used before non-defaulting Clearing Members default fund contributions are used.
The 4th line of defense shall, from a regulatory perspective, ensure prudent risk management of a CCP by exposing the CCP's equity to losses before socializing default losses to non-defaulting Clearing Members.
The current value of ECC's SITG is EUR 35 Mn.
5th Line of Defence: Default Fund
ECC has a Default Fund to cover losses exceeding those covered by margin requirements. The Default Fund is calibrated to cover the simultaneous default of the two clearing members to which ECC has the highest exposure under extreme but plausible market conditions. Each Clearing Member contributes to the Default Fund in proportion to its risk exposure.
The 6th line of defence aims at containing losses within the realm of ECC's members even in extreme market conditions. Moreover, the socialization of losses among Clearing Members provides sufficient incentives for them to support ECC in the management of a default.
Information on ECC's default fund contributions is provided in the current CPMI-IOSCO quantitative disclosure reports. Information on ECC's method to determine individual default fund contributions can be found under Stress Testing (ecc.de).
6th Line of Defence: ECC's Additional Dedicated Own Resources
ECC holds additional dedicated, freely available and liquid equity (also known as “Second Skin-in-the-Game” – SSITG) to be used in case of recovery measures requiring contributions of non-defaulting Clearing Members, e.g., Recovery Cash Calls or Partial Tear-Up.
As with the 4th line of defence, the 6th line of defence shall, from a regulatory perspective, ensure prudent risk management of a CCP by exposing the CCP's equity to additional losses before further contributions are called from non-defaulting Clearing Members. The current value of ECCs SSITG is EUR 15 Mn.
7th Line of Defence: Committed Additional Financial Resources
Clearing Members are committed to support ECC's management of a default event. ECC can request Clearing Members to provide additional financial resources to the default fund via a recovery cash call. For a Clearing Member, this is limited to one time the default fund contribution per default event and up to three times over a 90 -day period.
If ECC asks Clearing Members for a recovery cash call, ECC provides an additional voluntary contribution to its SITG and SSITG.
The 7th line of Defence aims at containing extreme losses beyond the stress scenarios expected within the realm of the Clearing System. ECC's additional voluntary contribution shows ECC's strong commitment to prudent risk management and incentives to see recovery cash calls as a last resort.
The potential (minimum) value of committed resources from a recovery cash call to non-defaulting Clearing Members can be found in the current CPMI-IOSCO quantitative disclosure reports.
The current value of ECCs additional voluntary committed contribution is EUR 50 Mn.
Default Waterfall